Gravity Based Systems
Gravity Based Structures have been used for many years, generally forming an artificial island which can be used as the base for facility installation.
The use of a Gravity Based System (GBS) for the storage of LNG and installation of the regasification facility had not been attempted previously. See the Adriatic LNG project.
The GBS philosophy enables the project to be constructed “off-location” and moved into position at a later date, with the potential to move the whole facility at a future date.
 GBS Outer Structure commences in dry dock
GBS Outer Structure commences in dry dock
The size of the GBS and the fact that it will be floated into it’s final position necessitates the use of a dry dock for construction. Prior to sail-away the dock will be flooded and the completed GBS will be towed to it’s final position and ballasted into position, forming an integrated LNG receiving and regasification structure.
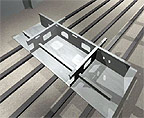 Fabrication of modular primary containment sections
Fabrication of modular primary containment sections
The primary containment vessels are fabricated elsewhere prior to installation into the GBS, enabling the use of specialist contractors with established facilities.
This philosophy also permits the parallel construction of the primary and secondary containment structures.
 Installation of the lateral trusses
Installation of the lateral trusses
The construction of the modular tanks lends itself to modularisation of internal components.
 1st Primary Containment section installed within the GBS
1st Primary Containment section installed within the GBS
Each primary containment vessel is constructed in 3 sections to facilitate transportation and installation into the GBS structure.
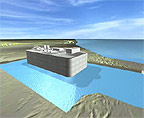 Dry dock flooded
Dry dock flooded
On completion of construction the dry dock will be flooded and the GBS floated out and towed to it’s operational location where it will be ballasted onto the sea bed and commissioned to receive and regasify LNG.

